Did You Know?
Advanced visual search system powered by Ajax
Advanced visual search system powered by Ajax
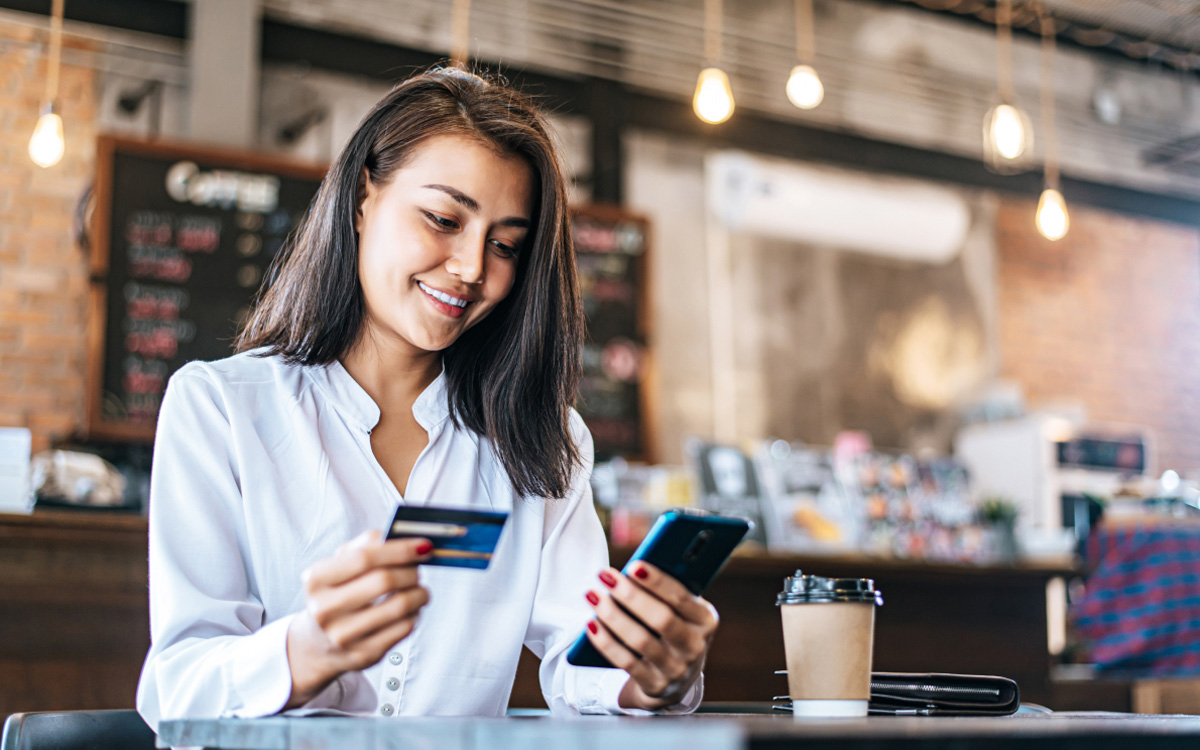

In the world of entrepreneurship, the relationship between personal finances and business finances is intricate and often intertwined. Understanding how to effectively link and manage both can be crucial to the success and stability of your business venture. This comprehensive guide will explore various aspects of linking your finances and your business, providing detailed insights, practical tips, and reference links to help you navigate this critical aspect of entrepreneurship.
Defining Personal and Business Finances
Personal finances refer to the management of an individual’s money, including income, expenses, savings, and investments. Business finances, on the other hand, involve the financial management of a business entity, encompassing revenue, expenses, profit margins, cash flow, and investments.
The Intersection of Personal and Business Finances
For many entrepreneurs, especially those running small businesses or startups, personal and business finances can overlap. This overlap can occur due to personal investments in the business, the use of personal credit for business purposes, or the lack of a clear distinction between personal and business expenses.
Key Principles
Legal Protection
Separating personal and business finances can provide legal protection by ensuring that personal assets are not at risk if the business faces legal issues or bankruptcy. This separation is particularly crucial for limited liability companies (LLCs) and corporations.
Tax Benefits
Clear separation of finances simplifies tax filing and helps in maximizing deductions and credits for both personal and business taxes.
Financial Clarity
Separating finances provides a clear picture of the financial health of both personal and business entities, aiding in better financial planning and decision-making.
Professionalism
Maintaining separate finances enhances the professionalism and credibility of the business, which can be beneficial when seeking investments or loans.
Choosing the Right Business Structure
The choice of business structure (sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, corporation) affects how you manage finances and your personal liability. Each structure has its advantages and implications for financial management.
Opening a Business Bank Account
A dedicated business bank account is essential for separating personal and business finances. It simplifies financial tracking, tax reporting, and provides a professional image.
Setting Up Accounting Systems
Implementing an accounting system (manual or software-based) helps in tracking income, expenses, and financial performance. Popular accounting software includes QuickBooks, Xero, and FreshBooks.
Hiring Financial Professionals
Consider hiring accountants, bookkeepers, or financial advisors to manage your business finances effectively and ensure compliance with financial regulations.
Budgeting
Create a personal budget that accounts for both personal and business income and expenses. This budget helps in maintaining financial stability and planning for future needs.
Emergency Fund
Maintain an emergency fund to cover unexpected personal expenses or business downturns. A good rule of thumb is to have at least three to six months’ worth of living expenses saved.
Investments
Diversify personal investments to reduce financial risk. Consider various investment options such as stocks, bonds, real estate, and retirement accounts.
Debt Management
Manage personal debt effectively to avoid financial stress. Prioritize paying off high-interest debt and consider consolidating debts for better management.
Personal Savings
Many entrepreneurs use personal savings to finance their business initially. This option provides full control but involves significant personal risk.
Business Loans
Business loans from banks, credit unions, or online lenders can provide necessary capital. Understand the terms, interest rates, and repayment schedules before committing.
Credit Cards
Business credit cards can be useful for managing short-term expenses. Ensure responsible usage to avoid high-interest debt.
Investors and Venture Capital
Seek investors or venture capital for significant funding needs. This option often involves giving up a portion of ownership and control but can provide substantial financial backing.
Grants and Crowdfunding
Explore grants and crowdfunding platforms (e.g., Kickstarter, Indiegogo) as alternative funding sources. These options can provide funds without the need for repayment or equity loss.
Understanding Tax Obligations
Know your tax obligations for both personal and business finances. This includes income tax, self-employment tax, payroll tax, and sales tax.
Deductions and Credits
Maximize deductions and credits by keeping detailed records of expenses. Common deductions include home office expenses, travel, and equipment.
Estimated Taxes
Entrepreneurs often need to pay estimated taxes quarterly. Proper planning and financial forecasting can prevent underpayment penalties.
Tax Professionals
Consult tax professionals to ensure compliance and optimize tax strategies. They can provide valuable advice on tax planning and preparation.
Establishing Business Credit
Start by opening a business credit card and using it responsibly. Pay bills on time and keep credit utilization low.
Credit Reporting Agencies
Monitor your business credit score through credit reporting agencies such as Dun & Bradstreet, Experian, and Equifax.
Vendor Relationships
Build relationships with vendors that report to credit agencies. Timely payments to these vendors can positively impact your credit score.
Loans and Lines of Credit
Consider small business loans or lines of credit to establish a credit history. Ensure timely repayments to build a positive credit profile.
Business Plan
A comprehensive business plan outlines financial goals, revenue projections, and expenses. Regularly update the plan to reflect changes in the business environment.
Cash Flow Management
Monitor cash flow to ensure the business can meet its financial obligations. Implement strategies to improve cash flow, such as timely invoicing and managing receivables.
Budgeting
Create a detailed budget that includes all business expenses and projected income. Regularly review and adjust the budget to stay on track.
Financial Forecasting
Use financial forecasting to predict future financial performance. This helps in planning for growth, managing risks, and making informed decisions.
Reinvestment
Reinvest profits into the business to fuel growth. This can include expanding operations, purchasing new equipment, or increasing marketing efforts.
Diversification
Diversify investments to spread risk. Consider investing in other businesses, stocks, bonds, or real estate.
Retirement Planning
Plan for retirement by contributing to retirement accounts such as a 401(k) or IRA. This ensures financial security in the long term.
Passive Income
Explore opportunities for passive income, such as rental properties, dividends from stocks, or online businesses. This can provide additional financial stability.
Identifying Risks
Identify potential risks to the business, including financial, operational, and market risks. Develop strategies to mitigate these risks.
Insurance
Purchase appropriate insurance coverage to protect the business. This may include general liability, property, workers’ compensation, and professional liability insurance.
Legal Protection
Implement legal safeguards such as contracts, trademarks, and patents to protect the business. Consult legal professionals for advice and assistance.
Emergency Planning
Develop an emergency plan to address unforeseen events such as natural disasters, economic downturns, or health crises. This plan should include financial contingencies and recovery strategies.
Accounting Software
Utilize accounting software to manage financial transactions, generate reports, and streamline tax preparation.
Financial Management Tools
Use financial management tools such as budgeting apps, expense trackers, and financial dashboards to monitor and control finances.
Payment Processing
Implement efficient payment processing systems to facilitate transactions and improve cash flow.
Security
Ensure the security of financial data by using encryption, secure networks, and regular backups. Protect against fraud and cyber threats.
Cash Flow Issues
Cash flow problems can hinder business operations. Address these issues by optimizing invoicing, managing receivables, and securing short-term financing.
Debt Management
High levels of debt can strain finances. Develop a repayment plan, consolidate debts, and prioritize high-interest debt.
Financial Mismanagement
Lack of financial expertise can lead to mismanagement. Invest in financial education, hire professionals, and implement robust financial systems.
Economic Fluctuations
Economic changes can impact business performance. Diversify income sources, maintain an emergency fund, and stay informed about market trends.
Case Study 1: Tech Startup
A tech startup successfully linked personal and business finances by securing seed funding, managing cash flow effectively, and reinvesting profits into product development. The founders maintained financial discipline and sought professional advice to navigate tax and legal complexities.
Case Study 2: Retail Business
A retail business faced financial challenges due to economic downturns. By separating personal and business finances, securing a business loan, and implementing cost-saving measures, the business managed to stabilize and eventually thrive.
Case Study 3: Freelance Consultant
A freelance consultant struggled with inconsistent income. By creating a detailed budget, building an emergency fund, and diversifying income streams, the consultant achieved financial stability and business growth.
Q1: Why is it important to separate personal and business finances?
Separating personal and business finances provides legal protection, simplifies tax filing, and offers financial clarity and professionalism.
Q2: What are some common methods of financing a business?
Common methods include personal savings, business loans, credit cards, investors, venture capital, grants, and crowdfunding.
Q3: How can I build business credit?
Establish business credit by opening a business credit card, maintaining timely payments, building vendor relationships, and monitoring your credit score.
Q4: What are the tax implications of linked finances?
Linked finances can complicate tax filing. Proper separation, detailed record-keeping, and consulting tax professionals can help manage tax obligations.
Q5: What tools can help in managing business finances?
Accounting software, financial management tools, payment processing systems, and security measures can streamline financial management.
Linking your finances and your business requires careful planning, disciplined management, and a clear understanding of financial principles. By separating personal and business finances, utilizing appropriate financial tools, and seeking professional advice, entrepreneurs can achieve financial stability and drive business success.
This guide provides an in-depth look at the critical aspects of linking personal and business finances. By following the principles and strategies outlined, entrepreneurs can navigate the complexities of financial management and build a successful business foundation.
Tomfoolery crikey bits and bobs brilliant bamboozled do...
Tomfoolery crikey bits and bobs brilliant bamboozled do...
Banca is a leading bank in the worldzone and a prominent international banking institution
COTATION
2023-01-05 14:00 (INTERNATIONAL TIME)